Plant-microbe interactions: Symbiotic relationships in plants
 Through evolution plants have developed sophisticated strategies to secure protection from biotic and abiotic stresses and availability of nutrients
Through evolution plants have developed sophisticated strategies to secure protection from biotic and abiotic stresses and availability of nutrients
Plant-microbe Interactions: Benefecial fungal endophytes
 Research in the lab focuses on endophytes-bacteria and fungi that live inter- and intracellularly in plants without inducing pathogenic symptoms and interact with the host biochemically and genetically.
Research in the lab focuses on endophytes-bacteria and fungi that live inter- and intracellularly in plants without inducing pathogenic symptoms and interact with the host biochemically and genetically.
Specialized metabolites in plants
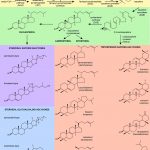 Plant metabolism is usually differentiated into primary and secondary metabolism. Secondary metabolites (also known as natural products, phytochemicals or specialized metabolites) underpin important plant traits (e.g. resistance, abiotic stress tolerance, nutritional quality and flavour).
Plant metabolism is usually differentiated into primary and secondary metabolism. Secondary metabolites (also known as natural products, phytochemicals or specialized metabolites) underpin important plant traits (e.g. resistance, abiotic stress tolerance, nutritional quality and flavour).
RNA interference In this research platform we aim to analyze RNAi-based gene regulation phenomena in plants and fungi. Plant-microbe interactions: Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi Plant microbiome: its role and its interactions with the agricultural environment Interactions of veterinary drugs (antibiotics and anthelmintics) with the soil microbiota Microbial degradation of pesticides contained in wastewaters from fruit-packaging plants: metabolic pathways, genetic mechanisms and potential applications Assessing the toxicity of pesticides on soil microorganisms Toxicity of pesticides onto non target organisms is an indispensable part of the pesticide regulatory framework. Although advanced protocols and tools have been developed and used for the assessment of the toxicity of pesticides on aquatic organisms and terrestrial macro-organisms this is not the case for soil microorganisms N microbial cycling and nitrification inhibitors Microplastics and Nanoplastics in soil: Interactions with soil microorganisms and plastisphere ecological role and composition Synthetic microbial ecology, synthetic biology and functional metagenomics to optimize bioremediation processess Functional metagenomics constitute a powerful molecular tool which has facilitated the isolation of novel enzymes with high biotechnological interest. Pesticide soil dissipation process: Biodegradation, Enhanced biodegradation, and Applications Biodegradation of veterinary drugs (antibiotics and anthelmintics) as a method for alleviating environmental contamination and ARGs dispersal Ανάδειξη οινικής ταυτότητας του νομού Δράμας μέσα από ολιστικό χαρακτηρισμό του φυσικού και μικροβιακού περιβάλλοντος Σκοπός του προτεινόμενου έργου ήταν ο πλήρης χαρακτηρισμός του ρόλου του αβιοτικού και του μικροβιακού terroir της οινοπαραγωγικής ζώνης Δράμας με στόχο την παραγωγή οίνων υψηλής ποιότητας και προστιθέμενης αξίας από τις κυριότερες οινοποιήσιμες ποικιλίες αμπέλου που καλλιεργούνται στην περιοχή. Μελετήθηκαν οι λευκές ποικιλίες Sauvignon Blanc και Ασύρτικο και οι ερυθρές Αγιωργίτικο, Cabernet Sauvignon και Merlot. Metagenomic analysis of the bacterial population of stone surfaces of monuments and development of nano-biomaterials for the sustainable protection of cultural heritage (BIOFOS) The research project “Metagenomic analysis of the bacterial population of stone surfaces of monuments and development of nano-biomaterials for the sustainable protection of cultural heritage (BIOFOS)” aims to apply metagenomics and bioinformatics technologies for the qualitative and quantitative identification of microorganisms and enzymes which induce decay or which may contribute to the protection of stone surfaces of monuments.
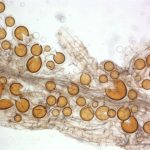 Plant symbiosis with AM fungi is very extensive in nature, most higher plants being mycorrhizal, and it is known to improve plant growth and nutrition, particularly regarding phosphorus but also to ameliorate drought stress and provide protection from pathogens.
Plant symbiosis with AM fungi is very extensive in nature, most higher plants being mycorrhizal, and it is known to improve plant growth and nutrition, particularly regarding phosphorus but also to ameliorate drought stress and provide protection from pathogens.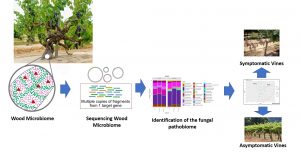 Microbes inhabiting plants exhibit different life styles ranging from pathogenic to beneficial. Several recent studies have highlighted the diversity of the microorganisms inhabiting plant parts and identified the significant role of epiphytic, endophytic and rhizospheric microbes on plants well-being.
Microbes inhabiting plants exhibit different life styles ranging from pathogenic to beneficial. Several recent studies have highlighted the diversity of the microorganisms inhabiting plant parts and identified the significant role of epiphytic, endophytic and rhizospheric microbes on plants well-being.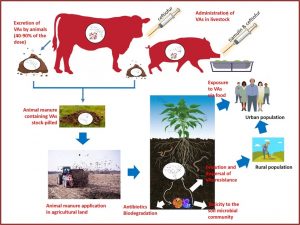 Veterinary antibiotics (VAs) and anthelmintics (AHs) are used to control microbial and parasitic infestations in livestock farming respectively. These compounds are not metabolized in the animals' body and are excreted at copious amounts in animal feces.
Veterinary antibiotics (VAs) and anthelmintics (AHs) are used to control microbial and parasitic infestations in livestock farming respectively. These compounds are not metabolized in the animals' body and are excreted at copious amounts in animal feces.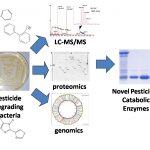 Postharvest treatment of fruits involves drenching or spraying with fungicides like thiabendazole, imazalil, ortho-phenylphenol and preservatives like diphenylamine and ethoxyquin.
Postharvest treatment of fruits involves drenching or spraying with fungicides like thiabendazole, imazalil, ortho-phenylphenol and preservatives like diphenylamine and ethoxyquin.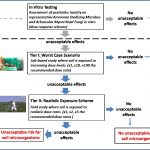
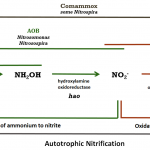 Nitrification is the rate-limiting step of N cycling. It is performed in two successive steps by ammonia oxidizing bacteria (ΑΟΒ) or archaea (ΑΟΑ), and nitrite oxidizing bacteria (ΝΟΒ). Recently, bacteria of the genus Nitrospira sp. (formerly known as ΝΟΒ) were found to be able to perform the complete oxidation of ammonia to nitrate, and they were named Comammox (Complete-ammonia-oxidation).
Nitrification is the rate-limiting step of N cycling. It is performed in two successive steps by ammonia oxidizing bacteria (ΑΟΒ) or archaea (ΑΟΑ), and nitrite oxidizing bacteria (ΝΟΒ). Recently, bacteria of the genus Nitrospira sp. (formerly known as ΝΟΒ) were found to be able to perform the complete oxidation of ammonia to nitrate, and they were named Comammox (Complete-ammonia-oxidation).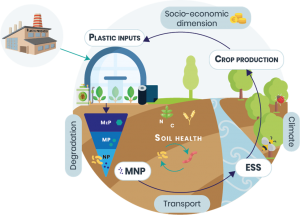 Microplastics (MP, plastic particles smaller than 5 mm) and nanoplastics (NP, smaller than 103 nm) are now considered emerging pollutants of global importance for agricultural soils, ranging in concentrations from 55.5 up to 593 particles per kg soil. They are small enough to be ingested by a wide range of organisms and at nano-scale, they can cross biological barriers and enter plants systems.
Microplastics (MP, plastic particles smaller than 5 mm) and nanoplastics (NP, smaller than 103 nm) are now considered emerging pollutants of global importance for agricultural soils, ranging in concentrations from 55.5 up to 593 particles per kg soil. They are small enough to be ingested by a wide range of organisms and at nano-scale, they can cross biological barriers and enter plants systems.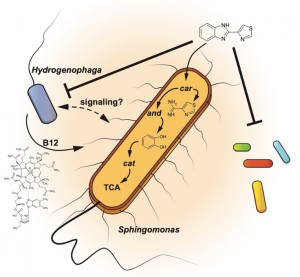
 Pesticides are common environmental contaminants. After their introduction in soil, pesticide dissipation is controlled by processes like degradation, biotic or abiotic, adsorption, volatilization and leaching.
Pesticides are common environmental contaminants. After their introduction in soil, pesticide dissipation is controlled by processes like degradation, biotic or abiotic, adsorption, volatilization and leaching. Veterinary antibiotics (VAs) and anthelmintics (AHs) are used to control microbial and parasitic infestations in livestock farming respectively. These compounds are not metabolized in the animals' body and animal excretes containing VAs and AHs are used as soil manures facilitating the dispersion of VA and AHs residues to agricultural soils.
Veterinary antibiotics (VAs) and anthelmintics (AHs) are used to control microbial and parasitic infestations in livestock farming respectively. These compounds are not metabolized in the animals' body and animal excretes containing VAs and AHs are used as soil manures facilitating the dispersion of VA and AHs residues to agricultural soils.